How to use a 32-bit driver program in 64‑bit Windows family of operating systems.
This information applies for the following operating systems:
Windows Server 2008 64-Bit Edition
Back Ground
I having been of late developing a Soft ware package in .NET Framework 3.5 for the LegaSync Project, to migrate the data from various legacy ERP systems (SAP,SYTELINE,MACPAC,MANMAN,JDE etc) to SQL server. The ODBC connectivity is used to retrieve the data from many of these legacy systems. Thus it involves various ODBC drivers, which all of them are designed for 32-bit platforms.
The initial development server that was hosted by the client was a 32-bit machine and we didn’t have any driver issues while connecting to the legacy systems.
But when it came to production deployment, the client had hosted a server with the latest configuration ( Windows Server 2008 R2, which was a 64 bit machine.)
It was then we came across this situation that 64-bit drivers need to be installed in the 64-bit machine.
But there are no 64-bit ODBC drivers available for those legacy systems in the market.
So we were in the situation that we need to install the existing 32-bit drivers in the 64-bit platform.
It was not possible to install legacy 32-bit installers to work on 64-bit Windows simply by running the installer package. The installer displays an informative error message.
The below trick cracked the issue of the installation of 32-bit driver in 64-bit platform.
Installation Considerations for 64-bit Platforms
Installation of 32-bit drivers in 64-bit platforms involves the following steps:
1) Creation of DTS Package (DTSPkg1.dtsx) using SQL Server Business Intelligence Development Studio, Which will internally run the required setup exe.
2) The DTS package needs to be run in the 32-bit windows. (default 64-bit)
3) So I used dtexec.exe, an application which can launch the application/DTS package in 32-bit windows and 64 bit windows.
4) The 32-bit support dtexec.exe will be present in” D:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SQL Server\100\DTS\Binn” and the 64-bit support dtexec.exe will be present in “D:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\100\DTS\Binn”.
5) The folder name ends with (x86) contains the 32-bit support files
6) Then I defined a new Sql Server Job in Sql server 2008 management studio
7) In the job step creation I selected the cmdExec as operating system and typed the following command:
"D:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SQL Server\100\DTS\Binn\dtexec.exe" /File "C:\DTSPkg\DTSPkg1.dtsx "
Then I ran the SQL Job. The 32-bit driver made a successful transition to the 64-bit operating system.
Viewing installed 32-bit drivers in 64-bit platform:
As the Windows 2008 supports both 32-bit and 64-bit, when we click on Data Sources (ODBC) From Program Menu/Control Panel, we cannot see the installed 32-bit drivers as it will display only the 64-bit drivers.

The reason is that the exe runs from System32 Folder (64-bit drivers)
To view the 32-bit drivers we need to type the following the command prompt
Ø %WINDIR%\SysWow64\odbcad32.exe
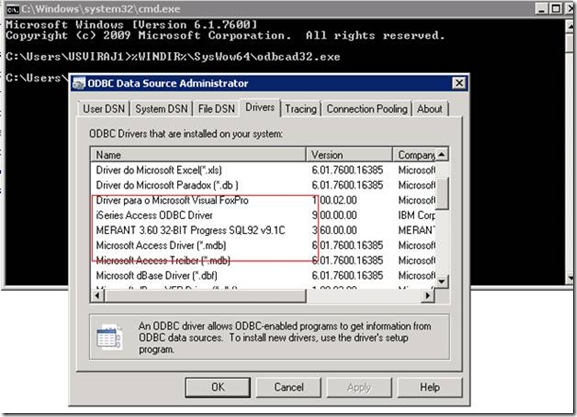
In the above picture is highlighted, a MERANT 3.60 32 –BIT Progress SQL92 V91.1 C which is the required ODBC driver for connecting Progress Databases of SYTELINE ERP’s to SQL Server
Migration of Windows 32-bit mode .NET application to 64-bit platform:
After the installation of 32-bit drivers in 64-bit platform, the next problem was the migration of the .Net application which was developed in 32-bit mode to the new 64-bit machine.
When I start running my application to connect with the legacy database, I got the following informative error:
“error[ im014] [Microsoft][ODBC Driver Manager]The specified DSN contains an architecture mismatch between the Driver and Application”
The error clearly indicates the architecture difference between the LegaSync application and New 64-bit Server and the application needs to be run in X86 architecture (32-bit platform)
Solution:
Creating platform specific apps
Most of the language compilers (like C#) now offer a /platform switch. By using this switch, developers can create binaries targeted for a specific platform type or binaries that are platform agnostic. There are four types of binaries that are emitted
· any cpu – platform agnostic
· x86 – 32-bit platform specific
· x64 – x64 platform specific
By default the compilers (like C#) emit anycpu binaries (also called portable assemblies) which are platform agnostic. In case the users want to create binaries specific to a platform, they can use the appropriate switch and be done.
Cross Compilation
The above concept of /platform switch enables cross compilation of binaries. Cross compilation means compiling binaries to a specific platform type (different from the current platform). This is mostly used in terms of compiling and creating 64-bit assemblies from a 32-bit compiler and vice versa. One point to note here is that cross compilation usually refers to compiling to different target types from the compilers shipped with the 64-bit Redist (WoW and 64-bit). The reason for this is that, while trying to compile for a 64-bit platform from a pure 32-bit machine, the 32-bit Redist would not have the components that are 64-bit specific. In such cases the compilation might go through with warning but execution might lead to runtime exceptions. Also, one should note that while cross compiling, users should stick to the platform architecture type of the machine, viz. x64 or IA. Assemblies for IA and x64 are specific to the platform architecture and cross compilation across architectures is not advised.
How to create platform specific apps?
Steps:
1) Go to Project->Properties->Compile
2) Click On Advanced Compile Options button
3) Change the Target CPU to X86 /X64 – default Any CPU
4) Rebuild the application
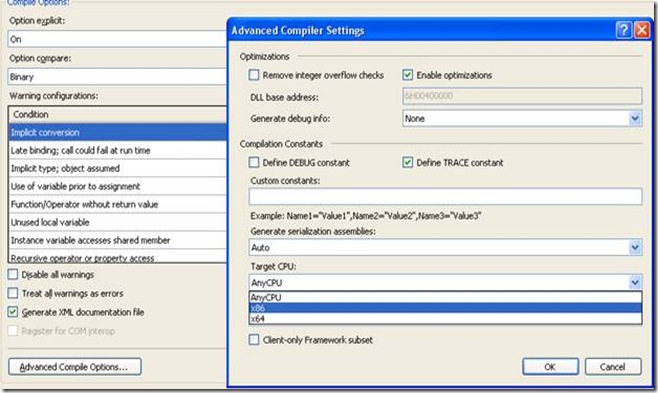
As I wanted the application to run in 32-bit mode in Compatible with X86 architecture, I Chose X86 CPU Compile Options.
The application started working fine.


